The Real-Time Data integration method enables partners to apply real-time enrichment decisions during auction processing. This integration method allows partners to analyze an incoming OpenRTB request and response and return enrichment signals that influence how the auction is evaluated. These enrichment decisions may be applied at different stages of an OpenRTB auction, such as at the Media Owner slot level or during DSP bid response processing.
Depending on the implementation model and supported capabilities, partners may provide enrichment such as:
User-level signals (for example, audience segments or cohorts)
Impression-level decisions (for example, activating or suppressing eligible deals)
Content-level metadata (for example, contextual attributes) (coming soon)
Bid-level modifications (for example, bid shading or price adjustments)
These services can be hosted by the partner or deployed in the Index Cloud.
How does it work?
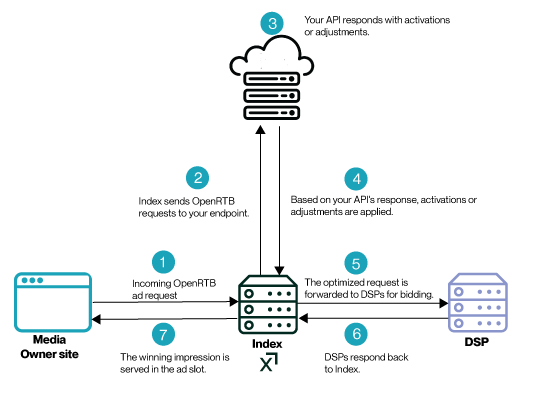
| A user visits a media owner's site, triggering an OpenRTB ad request that is sent to Index. |
| Based on implementation guidelines, Index sendsOpenRTB structured requests to the API endpoints exposed by your container. |
| Your API returns a structured response specifying decisions related to segment and deal activations, as well as pricing and scoring adjustments. The response format depends on the integration model (JSON for HTTP integrations, structured mutations for gRPC integrations). |
| Based on your API's response, activations and adjustment decisions are applied based on the model output. |
| The optimized request is forwarded to DSPs for bidding. |
| DSPs send bid responses back to Index |
| The winning impression is served in the ad slot. |
Integration implementation options
The real-time data integration supports the following transport implementations:
gRPC-based implementations (recommended): Enrichment decisions are returned as structured mutations defined by the agenticRTB Protocol Buffers schema.
HTTP-based implementations (legacy): Enrichment decisions are returned using JSON over HTTP. This model supports signal-level enrichment only. Existing integrations remain supported, but no new capabilities will be added.
Functionality comparison of gRPC and HTTP
| RTD concept | HTTP integration | gRPC integration |
|---|---|---|
Signal enrichment |
|
|
Deal eligibility | ❌ |
|
Content metadata | ❌ |
|
Bid price modification | ❌ |
|
Deal floor modification | ❌ |
|
Encoding | JSON | Protobuf |
Errors | HTTP status codes | gRPC status |







